What is Condensation?
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
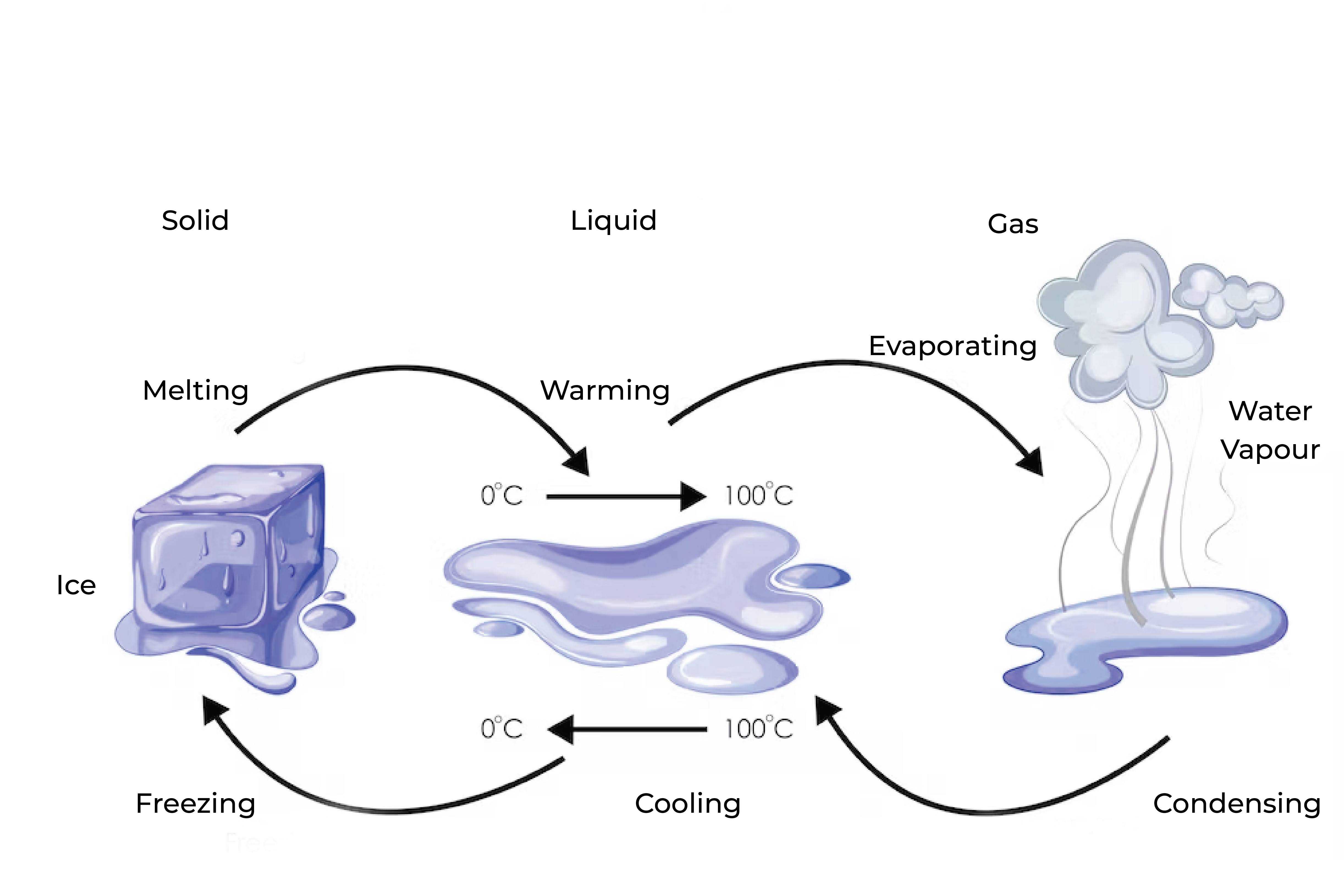
Condensation is the process by which a gas or vapor changes to a liquid state. This occurs when the gas or vapor loses heat energy and the particles slow down and come closer together, eventually forming a liquid.
What is Condensation? - Grade 6 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
|
Untimed |
|
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
Condensation can happen naturally in the atmosphere, such as when water vapor in the air cools and forms clouds or dew, or it can be induced artificially through cooling or compression of a gas. The opposite of condensation is evaporation, which is the process by which a liquid changes to a gas or vapor state.
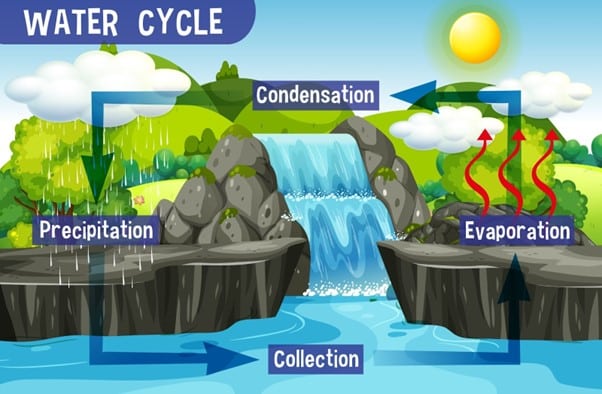
What are the physical conditions required for condensation
For condensation to occur, the following physical conditions are required:

Temperature: The temperature of the gas or vapor must be reduced below its saturation point, which is the temperature at which it becomes saturated with water vapor or other components. When the temperature drops below this point, the gas or vapor can no longer hold all of the water vapor or other components in the gaseous state, and it begins to condense.
Pressure: The pressure of the gas or vapor must remain constant or increase slightly, as this can help to keep the gas or vapor particles closer together and increase the likelihood of collisions that can lead to condensation.
Water vapor or other components: The gas or vapor must contain water vapor or other components that can condense under the given temperature and pressure conditions.
In summary, condensation requires the temperature to be lowered below the saturation point, the pressure to remain constant or increase slightly, and the gas or vapor to contain water vapor or other components that can condense.
What are Chemical Conditions Required for Condensation?
Condensation is a physical process, not a chemical process, so it does not require any specific chemical conditions to occur.
However, certain chemical reactions can produce water vapor or other gasses that can undergo condensation under the appropriate physical conditions of temperature and pressure.
For example, the combustion of fuels such as natural gas or gasoline can produce water vapor as a byproduct, which can undergo condensation when the temperature and pressure are appropriate.
Similarly, chemical reactions that produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other gasses can also result in condensation when the conditions are right.
However, in general, the chemical conditions required for condensation are simply the conditions that produce the gas or vapor in the first place, and the subsequent condensation is driven by the physical conditions.
Molecular Process of Condensation
The molecular process of condensation involves the transition of gas or vapor molecules to a liquid state.
At the molecular level, gas molecules are in a highly disordered and random motion, with high kinetic energy and widely separated from one another.
As the gas or vapor is cooled, the kinetic energy of the molecules decreases, causing them to slow down and move closer together.
When the temperature drops below the saturation point, the gas or vapor becomes supersaturated and the molecules begin to come into closer proximity.
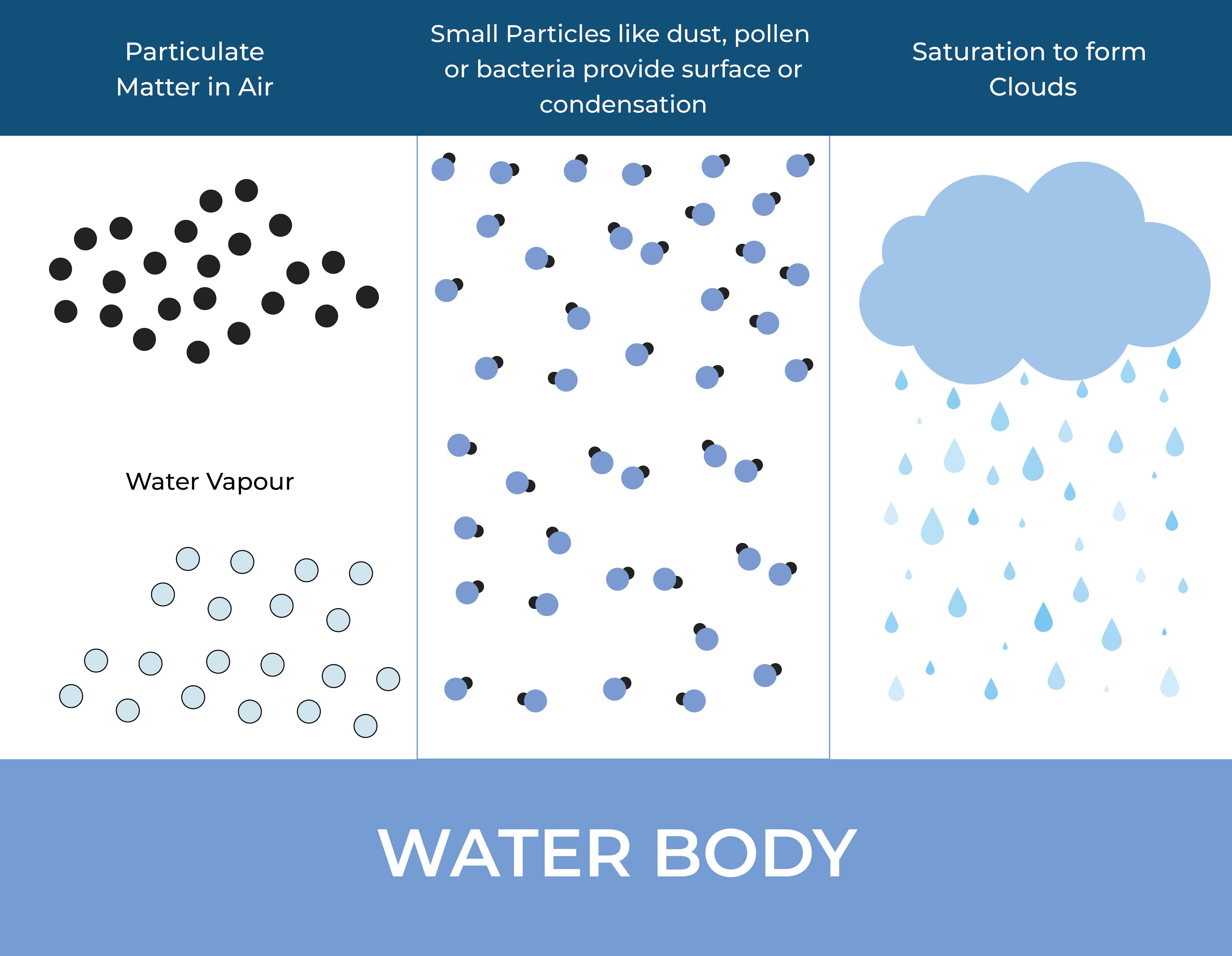
When two gas molecules come close enough, they may form a weak intermolecular attraction known as Van der Waals forces. As more and more molecules come close together, these intermolecular forces become stronger and more stable, eventually leading to the formation of liquid droplets.
The newly formed liquid droplets continue to attract more gas molecules, which can continue to condense onto the surface of the droplets, causing them to grow in size.
The process of condensation is an exothermic process, which means that heat is released during the process. The heat released is the same amount that was absorbed during the process of evaporation, which is the opposite process of condensation.
What is the Difference between Solidification & Condensation?
Solidification and condensation are both physical processes that involve a change of state, but they differ in several key ways:
Phase change: Solidification involves a change from a liquid to a solid state, while condensation involves a change from a gas or vapor to a liquid state.
Energy transfer: Solidification involves the release of heat energy, while condensation involves the absorption of heat energy. When a liquid solidifies, it gives off heat energy as it cools and the particles slow down and come closer together. When a gas condenses, it absorbs heat energy as it cools and the particles slow down and come closer together.
Particle arrangement: In solidification, the particles become tightly packed and arranged in a regular, repeating pattern to form a solid. In condensation, the particles become more densely packed but do not necessarily form a regular pattern.
Conditions: The physical conditions required for solidification and condensation are different. Solidification generally requires a decrease in temperature and/or an increase in pressure, while condensation generally requires a decrease in temperature and/or an increase in pressure, as well as the presence of a gas or vapor that can condense.
In summary, solidification and condensation are both physical processes that involve a change of state, but they differ in the phase change, energy transfer, particle arrangement, and physical conditions required.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
6th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $22.49 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
What is the Difference between Condensation & Chemical Reactions?
Condensation and chemical reactions are two different types of processes that involve the transformation of matter. The main differences between the two are:
Nature of the process: Condensation is a physical process, while chemical reactions are chemical processes.
Changes in the identity of the substance: In condensation, the identity of the substance does not change. The molecules simply change their state from gas to liquid. In chemical reactions, the identity of the substance changes, and new substances are formed.
Reversibility: Condensation is a reversible process. The liquid can be turned back into a gas by increasing the temperature or decreasing the pressure. Chemical reactions, on the other hand, are usually irreversible.
Here are some examples to illustrate the difference between condensation and chemical reactions:
Condensation: The formation of dew on a grassy field on a cool morning is an example of condensation. Water vapor in the air condenses onto the surface of the grass blades to form water droplets. The identity of the water molecule remains the same.
Chemical reaction: The rusting of iron is an example of a chemical reaction. When iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of water, a new substance (iron oxide or rust) is formed. The identity of the iron molecule changes into iron oxide.
Examples of Condensation:
Condensation is a natural process that occurs in many different forms in nature. Here are some examples:
Cloud formation: Clouds are formed by the condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere. As moist air rises, it cools and the water vapor in the air begins to condense into tiny droplets, forming clouds.
Dew formation: Dew is formed when the temperature of the ground or other surfaces drops below the dew point temperature, causing water vapor in the air to condense into droplets on the surface.
Fog formation: Fog is formed by the same process as clouds, but at ground level. When moist air is cooled to the point of saturation, the water vapor in the air condenses into tiny droplets, forming fog.
Rain: Rain is formed when water droplets in clouds combine and become large enough to fall to the ground. This process involves the condensation of water vapor into liquid droplets.
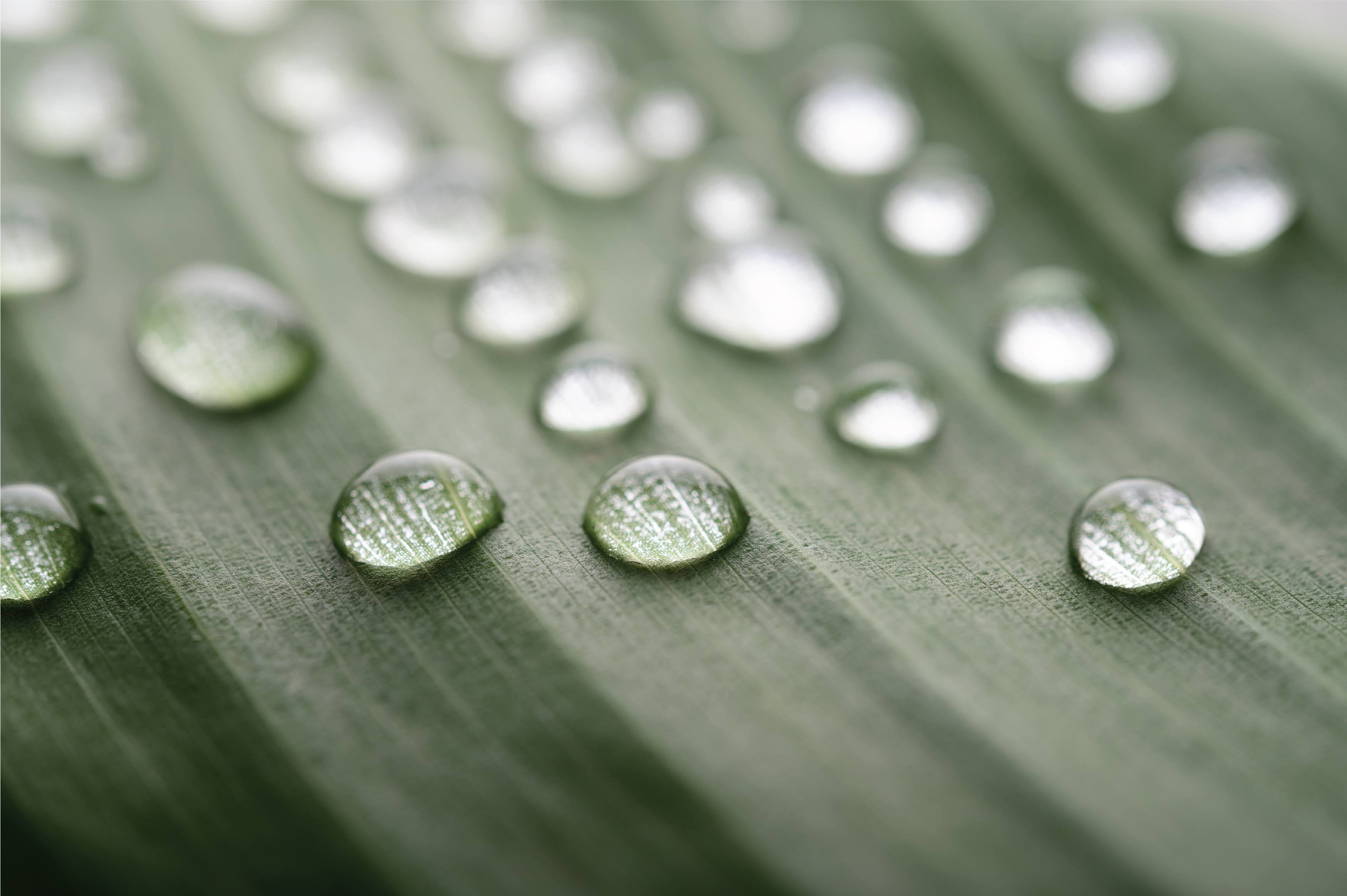

Formation of droplets on leaves: Water droplets can be seen on leaves and other surfaces on cool mornings. This occurs when water vapor in the air condenses onto the surface of the leaf or other object.
What are the Exceptions for Condensation ?
There are several exceptions to the process of condensation, including:
Sublimation: This is the process in which a solid changes directly to a gas without first becoming a liquid. This occurs when the vapor pressure of the solid exceeds the pressure of the surrounding environment, such as in the case of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) turning into gas.
Deposition: This is the opposite of sublimation, where a gas or vapor changes directly to a solid without becoming a liquid. This can occur when the temperature of the gas or vapor drops below its freezing point, causing the molecules to lose kinetic energy and bond together to form a solid.
Supersaturation: This is when the concentration of a gas or vapor in the air exceeds its saturation level, but condensation does not occur. This can occur in certain conditions such as when the air is very dry, or when the temperature changes very quickly.
Hydrophobic surfaces: These are surfaces that are highly water-repellent, such as certain types of plant leaves or synthetic materials. Water droplets on these surfaces tend to bead up and roll off rather than adhering and condensing into a liquid film.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
FAQS
What is condensation?
Condensation is the process by which a gas or vapor changes its physical state to a liquid. This occurs when the gas or vapor is cooled or compressed to a point where its molecules lose kinetic energy and can come together to form a liquid.
What are some examples of condensation?
Some examples of condensation include the formation of dew on grass, the formation of fog and clouds in the atmosphere, the formation of water droplets on a cold drink glass, and the formation of rain from clouds.
What is the difference between condensation and evaporation?
Condensation and evaporation are opposite processes. Condensation is the process by which a gas or vapor changes to a liquid, while evaporation is the process by which a liquid changes to a gas or vapor.
What factors affect the rate of condensation?
The rate of condensation can be affected by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the concentration of the gas or vapor in the air.
Is condensation a physical or chemical change?
Condensation is a physical change, as the identity of the substance does not change. The molecules simply change their state from gas to liquid.
What is the role of condensation in the water cycle?
Condensation plays a key role in the water cycle. Water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid droplets to form clouds, which can then produce precipitation in the form of rain or snow. This precipitation can then replenish bodies of water and eventually evaporate, continuing the water cycle.
Can condensation cause problems in buildings?
Condensation can be a problem in buildings, particularly in areas with high humidity. It can lead to the growth of mold and mildew, which can cause health problems and damage to the building materials.
How can condensation be prevented?
Condensation can be prevented by controlling the temperature and humidity in the environment. This can be done through proper ventilation, insulation, and the use of dehumidifiers or air conditioning.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










