Reproduction in Plants
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
In this article, we will explore the various modes of reproduction in plants, from the production of seeds to vegetative propagation. We will also examine the advantages and disadvantages of different methods of reproduction, and the role that reproduction plays in the survival and evolution of plant species. Whether you are a gardener, botanist, or simply interested in nature, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of reproduction in plants.
Table of Contents:
- Modes of Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants
- Asexual Reproduction in Plants
- FAQs
Reproduction in Plants - Grade 7 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
|
Untimed |
|
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
Plants play a vital role in our ecosystem and are essential for life on Earth. They are the primary source of food, oxygen, and medicine for many species, including humans. Reproduction is a critical aspect of plant life, as it allows for the continuation of the species and the spread of their genetic information.
Modes of Reproduction
There are two modes of reproduction in plants:
1. Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of cells called gametes, which are produced by different parts of the same plant or by different plants. This results in the creation of new offspring that have genetic information from both parents.
For example, in flowering plants (Angiosperms), the male gamete is produced by the stamen, which is the male reproductive organ. The female gamete is produced by the pistil, which is the female reproductive organ. When the male gamete reaches the female gamete, fertilization takes place, and a seed is formed.
Another example is in ferns, where the male gamete is produced by the sporangium and the female gamete is produced by the archegonium. Fertilization takes place when the male gamete reaches the female gamete, and a new fern plant is produced.

In both flowering plants and ferns, the new plant that is produced from sexual reproduction is genetically unique, as it contains genetic information from both parents. This helps to create genetic diversity in a species, which can be important for its survival in changing environments.
In plants, the reproductive part is the flower, which is responsible for producing seeds that can grow into new plants. Flowers contain male and female reproductive structures, such as stamens and pistils, which are involved in pollination and fertilization.
The vegetative parts of a plant include the roots, stem, and leaves, which are responsible for the plant’s growth and survival. Roots anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and nutrients, while the stem provides support and transports water and nutrients to other parts of the plant.
Leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis, where they capture light energy and use it to produce food for the plant. Vegetative parts can also give rise to new plants through asexual reproduction, such as when a stem or leaf cutting is used to grow a new plant which are similar to their parents.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
7th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $21 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
2. Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Asexual reproduction in plants is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of cells from two different individuals. Instead, a new plant is produced from a single individual. This reproduction type results in genetically identical offspring to the parent plant.
For example, in some plants such as strawberries, a new plant can grow from a runner, a stem that grows out of the parent plant and takes root elsewhere. This new plant is a genetic copy of the parent plant.
Asexual reproduction in plants is the process of producing new individuals without the involvement of gametes or the fusion of male and female reproductive cells.
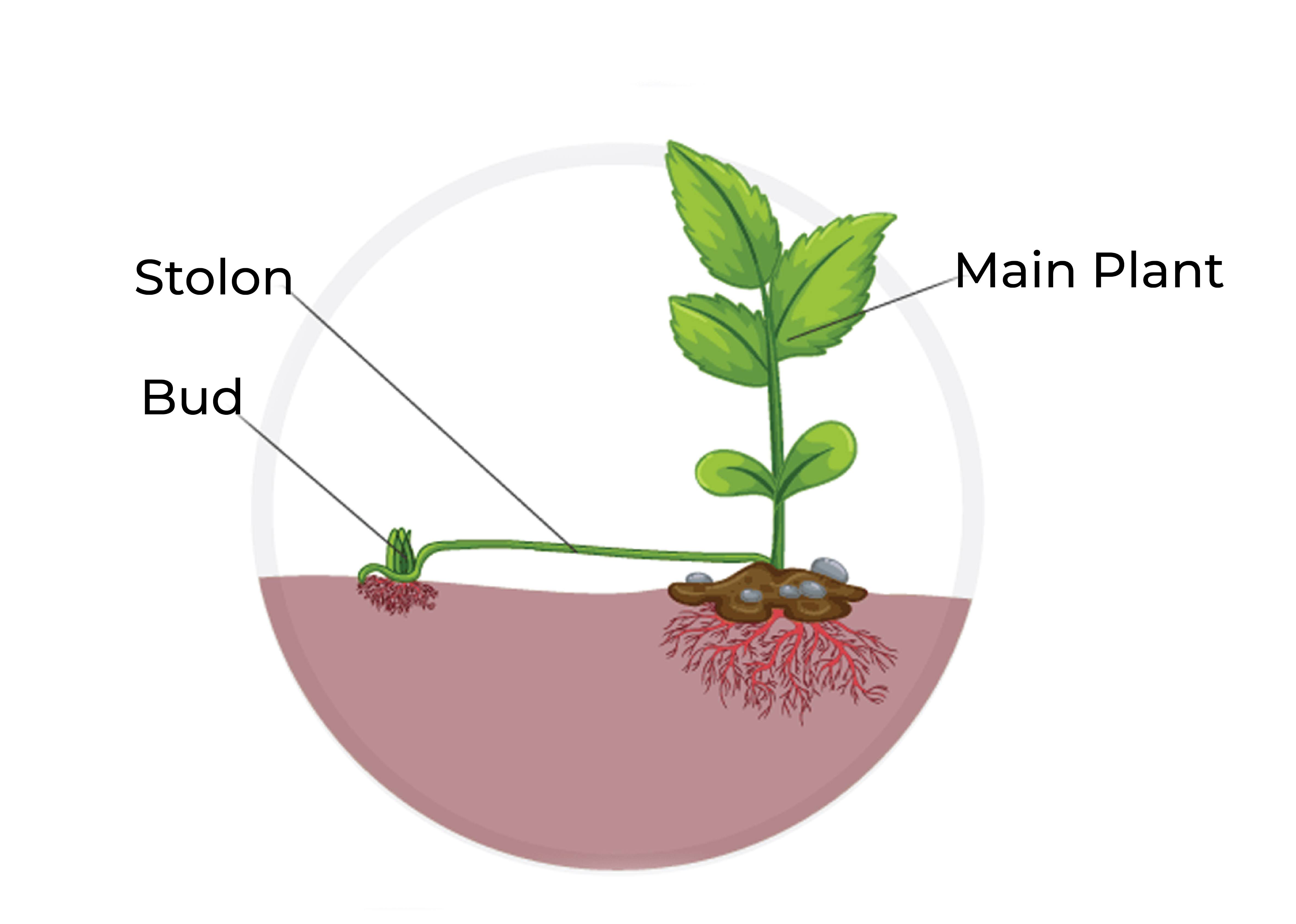
There are several types of asexual reproduction in plants, including:
- Fragmentation: In this type of asexual reproduction, a part of the plant, such as a stem, leaf, or root, breaks off and forms a new individual. Examples of plants that can reproduce through fragmentation include spider plants, strawberry plants, and some types of ferns.
- Vegetative Propagation: This involves the production of new individuals from vegetative structures, such as stems, leaves, and roots.
Some examples of vegetative propagation include:
Runners: Plants such as strawberries produce horizontal stems that produce new plants at nodes along the stem.
Bulbs: Onions and garlic produce bulbs that can be planted to produce new plants.
Tubers: Potatoes produce underground tubers that can be planted to produce new plants.
Rhizomes: Iris plants produce rhizomes, which are underground stems that produce new plants at nodes along the stem.
Apomixis: This is a type of asexual reproduction in which seeds are produced without fertilization. The offspring are genetically identical to the parent plant. Examples of plants that can reproduce through apomixis include dandelions, blackberries, and some species of grasses.
Asexual reproduction allows plants to quickly produce new individuals without the need for a mate. This can be advantageous in environments where sexual reproduction may be difficult due to factors such as isolation or limited resources.
Another example is in some types of moss, where a new plant can grow from a piece of the parent plant that has broken off and taken root. This new plant is also a genetic copy of the parent plant.
In both of these examples, the new plant produced from asexual reproduction is identical to the parent plant. This type of reproduction can be useful for the plant in certain situations, such as when it is difficult to find a mate, or when it needs to spread quickly to a new area.
However, asexual reproduction does not create genetic diversity, which can be important for the survival of a species in changing environments.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
Reproduction in Plants FAQS
What is reproduction in plants?
Reproduction in plants refers to the process by which new individuals are produced from existing plants. There are two main types of reproduction in plants: sexual and asexual.
What is sexual reproduction in plants?
Sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of cells called gametes from different parts of the same plant or from different plants. This results in the creation of new offspring that have genetic information from both parents.
What is asexual reproduction in plants?
Asexual reproduction in plants is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of cells from two different individuals. Instead, a new plant is produced from a single individual. This type of reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent plant.
What are some examples of asexual reproduction in plants?
Examples of asexual reproduction in plants include runners in strawberries, vegetative propagation in some types of trees, and division in some types of moss.
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction in plants?
The advantages of sexual reproduction in plants include increased genetic diversity, which can improve the species’ adaptability to changing environments, and the ability to recombine favorable traits from different parents.
What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction in plants?
The disadvantages of asexual reproduction in plants include the lack of genetic diversity, which can limit the species’ adaptability to changing environments, and the potential for the accumulation of harmful mutations in the absence of recombination.
How does reproduction play a role in the survival of plant species?
Reproduction plays a crucial role in the survival of plant species by allowing the continuation of the species and the spread of their genetic information. Reproduction also allows for the creation of genetic diversity, which can improve the species’ adaptability to changing environments.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
- Elements and Compounds
- Solar Energy
- Photosynthesis
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Law of conservation of energy
- Periodic table
- Properties of Matter
- Waves
- Energy Resources
- Weather and Climate
- Immune, Circulatory and Digestive Systems
- Organs in Multi-cellular Organism
- Sedimentary, Igneous, and Metamorphic Rocks
- Structure of the Earth
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Scientific Method
- Human Digestive System
- Environmental Science
- Renewable and Non-renewable energy Resources
- Characteristics of Living Organisms
- Life Science
- Earth and Space Science
- Solar Eclipse
- Heat Technology
- Newton’s Laws of Motions
- Physical Science
- Tools, Measurement and SI Units
- Earth Atmosphere
- Interactions of Living things
- The Earth Ecosystem
- Organelles in Plant and Animal cells
- Layers of the Earth
- Cycles in Nature
Grade 7 Math Worksheets
- Fractions
- Linear equations word problems
- Statistics
- Properties of Parallel Line
- Finding slope from an equation
- Identifying Quadrilaterals
- Percent Change
- Properties of addition and multiplication
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Solving two step inequalities
- Symmetry
- Fractions to Decimals (New)
- Whole Number Exponents with Integer Bases (New)
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions (New)
- Integer Addition and Subtraction (New)
- Dividing Mixed Numbers (New)
- Basics of Coordinate Geometry (New)
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










